Intragastric Balloon Procedure
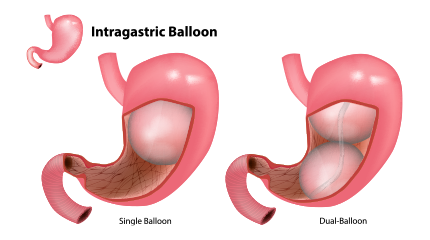
Intragastric Balloon procedure is used to facilitate weight loss; a balloon filled with liquid is placed in the patient's stomach; this procedure limits food intake making the patient feel full faster leading to gradual weight loss.
Weight loss not only allows patients to lead more active and comfortable lives but also reduces the risk of potentially serious weight-related diseases, such as:
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- cardiovascular diseases;
- high blood pressure;
- obstructive sleep apnea;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH);
- type 2 diabetes.
The Intragastric balloon procedure is an effective method of weight loss for patients;
- with a body mass index between 30 and 40,
- ready to follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle,
- Both female and male,
- with type 2 diabetes who cannot control sugar level due to being overweight,
- who are prohibited from having surgical intervention due to excess weight,
- who do not have enough financial resources to undergo other weight-loss surgeries,
- who, for various reasons, do not want to pursue surgical methods for their excess weight issues,
- who have not undergone any previous stomach or esophageal surgeries.
Using this procedure does not just help with weight loss. The placement of an intragastric balloon is recommended for patients who:
- are preparing for operations such as joint surgery, bariatric surgery, or gastric bypass surgery.
Here are the following contraindications for the placement of an intragastric balloon:
- diseases or abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract,
- malignant diseases,
- mental health disorders, as well as alcoholism and drug addiction,
- serious diseases of the vital organs,
- pregnancy and breastfeeding.
An intragastric balloon helps patients feel full faster by reducing portion sizes. An intragastric balloon slows down the process of gastric emptying and can alter the level of hormones that control appetite.
According to the results of studies, patients typically experience 7% to 15% weight loss within six months after intragastric balloon placement, and an overall excess weight loss range from 30% to 47%.
Other advantages of this operation include:
- it's minimally invasive.
- It doesn’t involve medication.
- There are limited complications.
The amount of weight loss also depends on patient's willingness to change their lifestyle habits including the increase of healthy eating and exercise.
Even the most effective and correctly performed procedure will not yield the desired results on its own if the patient does not follow the subsequent healthy eating and exercise recommendations.
Intragastric Balloon — Everything About the Procedure
Implementation of an intragastric balloon is performed on an outpatient basis and takes about half an hour. Depending on the type of selected intragastric balloon, the procedure can be performed without anesthesia or with anesthesia (intravenous or general). Patients can usually be discharged 1-2 hours after the procedure's completion; however, some clinics recommend an overnight stay in the hospital, where the patient can be observed under the supervision of doctors.
About six hours after the procedure, patients can drink a small amount of clear liquids. This liquid diet is usually continued until the beginning of the second week; subsequently, patients can begin to eat soft foods. Foods such as coffee, fatty foods, or soft drinks should be avoided during this period. Patients usually return to their normal eating and drinking habits about three weeks after the procedure.
Remember that each case is different; as a result, it is necessary for patients to follow individual plans for the transition to more solid foods. In some cases, patients prefer to keep a diary, recording progress in terms of nutrition and the gradual return to an active lifestyle, as well as observing the adaptation process of the body.
Although balloon placement is an effective obesity treatment , it is important to note the associated side effects. Pain and nausea occur in about a third of patients soon after the intragastric balloon is inserted; however, these symptoms usually last only a few days and can be managed at home with medications.
In rare cases, serious side effects can occur after inserting the intragastric balloon. If after the operation nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain occur, you should immediately speak to your doctor. There are other potential risks, such as balloon deflation or intolerance, acute pancreatitis, ulcers, and others.
One potential issue with patients is a lack of psychological readiness; after the balloon is removed, patients are left with the same size of the stomach. If the patient does not prepare for this stage and does not form new habits, the excess weight can return.
Patients who decide to have an intragastric balloon inserted should be thoroughly examined and prepared for the procedure, including a discussion with their doctor concerning lifestyle and medications; if patients do not actively exercise, it is important that they discuss the benefits of an active lifestyle.
An intragastric balloon is inserted for a period of 6 to 12 months (depending on the clinic and the chosen type), and its removal is as easy as its insertion. 2-3 hours after removal, the patient can return home, or, if desired, stay overnight in the clinic.
It is possible to re-insert the intragastric balloon; however, it is necessary to follow a 2-month break between procedures.
In most cases, patients suffering from obesity need a little push towards adopting a new, more comfortable life. Inserting an intragastric balloon helps patients to not only lose excess weight but it also assists in facilitating positive lifestyle changes.
In some cases, when patients are not ready to make positive adjustments in their lives, it is necessary to combine the procedure with training programs and explain clearly that the intragastric balloon alone will not lead to the desired weight loss. We can say with confidence that a balloon provides an opportunity for patients to make lasting improvements to their lives.
Intragastric Balloon — How to Get Prepared?
After consulting a doctor and conducting a preliminary assessment, patients are advised to prepare for the procedure by:
- informing family members about the planned procedure so that they can bring them home and look after them post-surgery;
- discussing preparation for the operation with their doctor 12 hours prior to its start time;
- finding out what foods need to be prepared for meals after being discharged from the clinic;
- planning periods of rest before and after the procedure.
Intragastric Balloon — FAQ
Can I drink alcoholic beverages?
After inserting an intragastric balloon, you can drink alcohol in moderation; it is best to discuss this in more detail with your doctor.
Can I eat sweets?
To achieve optimum results, we recommend limiting your sugar intake; it is possible that after having the balloon placed, you may feel worse when consuming sweets and other food items containing sugar.
